Thermodynamics of DNA hybridization
A combination of spectroscopy and
calorimetry was used to determine the free energies of melting of short oligonucleotides. Based on these measurements the free energy of a helix can be determined based on10
sets of nearest-neighbor pairs shown in Figure 16.5. In addition to these values we need to know
the free energy of the initiation (i.e. the first base pair). The overall free energy is then calculated
from:
DGo = DGo (initiation) + S
DGo (nearest neighbors)
Sample problem. Determine the melt
temperature for the oligonucleotide
5’-ATAGCA-3’
ß 5’-ATAGCA-3’
à 3’-TATCGT-5’
3’-TATCGT-5’
Solution:
DGo
= DGo (initiation) + S DGo
(nearest neighbors)
=
20.9 - 6.3 - 3.8 - 6.7 - 13.0 - 6.9
=
-16.8 kJ
Note that we use GC initiation if
there is a single GC base pair.
Only use AT initiation of the
strands are all A and T.
DGo = -16.8 kJ
Notice that the the free energy of
initiation is positive. Initiation is unfavorable
because of the entropy that must be overcome to bring the chains together. To calculate the melt temperature we need the
enthalpy of reaction as well.
=
- 36.0 - 25.1 - 32.6 - 46.4 - 24.3
= -164.4 kJ

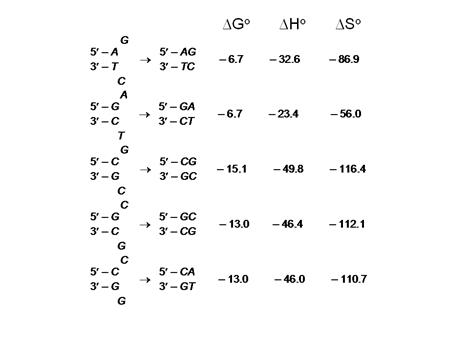
Figure 1. Thermodynamic data for
base pair formation. Each possible
combination of base pairs is given both for initiation and for internal
(nearest neighbor) configurations. Data
were obtained from Breslauer et al. PNAS, 93, 3746 (1986).
The data in Figure 1 can be used to
estimate the stability of a mutagenesis primer.
However, it can also be applied to the determination of the melt
temperature of a primer. The quantities DGo, DHo and DSo
are tabulated at 298 K. The
hybridization free energy, DGo,
decreases as the temperature is increased according to,
![]()
At the melt temperature, Tm,
![]() Therefore,
Therefore,
![]()
which implies that
![]()
Thus, the values in the
thermodynamic tables can also be used to estimate the melt temperature of an
oligonucleotide. Such determinations are
now routine in computer programs for commercial primer design for mutagenesis
protocols using the polymerase chain reaction.