Derivation
of the kinetic equation for CO recombination to deoxy
Mb
One can assume that the photolyzed
product Mb:CO is present
initially as shown in the figure (His-FeP:CO or Mb:CO). There are
two pathways shown with rate constants kgem
and kesc. gives
rise to the following rate scheme.
![]()
![]()
![]()
These equations cannot be solved
exactly. However, we can solve the
equation for the geminate state, Mb:CO,
which is immediately produced by photolysis.
The result is,
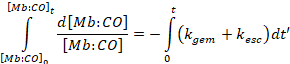
![]()
Since the rate constants kgem and kesc
>> kbi, we can approximately the
rate of formation of MbCO and the deoxy
Mb states as
![]()
![]()
Which leads to,
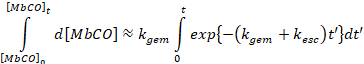
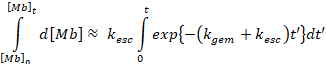
And
![]()
![]()
According to the myoglobin rate
scheme there is a quantum yield for both geminate recombination and
escape. These are,
![]()
Finally, we can determine the rate
of depletion of the deoxy state (i.e. bimolecular
recombination) from a separate equation,
![]()
Solution of the rate equations
Combining these equations leads to the overall time course
![]()
where the
prime indicates that this is a pseudo-first-order rate constant, ![]() . The pseudo-first order rate constant has the appearance
of a first order process at a fixed concentration of CO. Figure 1 shows how the
rate differs as the CO concentration is varied by a
factor of 10.
. The pseudo-first order rate constant has the appearance
of a first order process at a fixed concentration of CO. Figure 1 shows how the
rate differs as the CO concentration is varied by a
factor of 10.
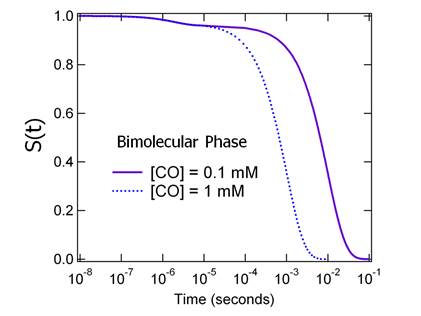
Figure
1 MbCO recombination kinetics showing the difference
between the geminate and bimolecular phases. The bimolecular phase is
pseudo-first order.