The structure of phthalocyanine (Pc) is shown in the figure. To understand the absorption spectra of Pc, one can use a free electron model for a particle on a circle assuming that there are 18 p-electrons contributing. In the free electron model you may assume that the electrons from the p-orbitals of the carbon atoms populate energy levels derived from the particle-on-a-circle solution to the Schrödinger equation. The major difference of Pc relative to the more common porphyrins is that the effective radius of the circle is larger.
A. Assuming that the radius of the circle is 4.3 Å and that the Pc has 18 electrons, please draw an energy level diagram for this system.
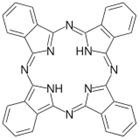
B. Calculate the maximum of the absorption spectrum (in nm).
lmax = __________________nm.
C. Pc was accidentally discovered in 1907. It was observed as a compound with a deep blue color. The absorbance of Pc was determined to be 0.7 in a 0.4 cm path length cell at its lmax when 8.1 mg of the compound was isolated from a volume of 1 liter. The molar mass of Pc is 514.5 grams/mol. Determine the molar extinction coefficient at the lmax of Pc.
Extinction coefficient (units!) = ____________________________.
D. What is the percent transmittance of the solution with an absorbance of 0.7?
Percent transmittance = ____________________________.